We are moving on with our series, Searching for the Truth on Origins, and we will examine the topic of our own origins, where we came from. In session number seven, we want to talk about the evolutionary perspective which is the belief that man has evolved from lower levels of consciousness. Of course the idea is that monkeys and apes are our cousins.
Again we begin with a portion of Scripture which I think is very relative to this presentation, Isaiah 55:8-9.
For My thoughts are not your thoughts. Nor are your ways My ways, says the Lord. For as the heavens are higher than the earth, so are My ways higher than your ways, and My thoughts than your thoughts.
In this presentation we are going to look at man’s thoughts regarding man’s origin. In the next session (session eight) we are going to look at God’s thoughts and human origins. And we are going to see that God’s thoughts compared to man’s thoughts (when it comes to this topic of human origins) are as high as the heavens are above the earth. These are two widely contrasting views.
Let us begin by examining some of the claims of the evolutionary worldview regarding human origins. First of all I want to look at this textbook called, Ape Man; The Story of Human Evolution. That is an interesting subtitle! You see, evolutionists claim that they are able to verify the lineage of man, that is, we have risen from these brute apelike creatures and that this can be done scientifically. Do you remember our definition of science? Science must be based on facts, observable evidence, and experimentation. We cannot rely upon stories. We must have physical, observable evidence. And through this presentation, I will emphasize that many things that are proposed to us in the name of science—like suggesting that we have evolved from these lower brute-like creatures—is based on wild speculation.
In the introduction of this book, there is a picture of Walter Cronkite. The reason is that Ape Man, the book, has also been made into a television series which I have seen. Here you see Walter Cronkite standing in front of an African church. The camera interviews Walter Cronkite and he makes a statement similar to this: "This documentary is going to search for the truth on the origin of man. While there are many people who believe that God created us..." and at that point the camera pans to a view inside the church where African natives are singing hymns and worshipping God. Cronkite said, "While we respect their beliefs, this documentary will show you scientifically that it has been proven that we have evolved." Well, Walter Cronkite is a rather influential person. In fact, videos like this and textbooks like this have influenced people worldwide into believing that we have evolved.
Here is a statement taken from the introduction of the book:
Based on interviews with leading scientists working all over the world, Ape Man explored the story of our evolution and of the people who have devoted their lives to discovering the truth about origins. (Caird)
Remember what our series is about? We are searching for the truth about origins. And as you can see, evolutionists believe that that is what they are doing and that they have discovered the truth about our origins.
And then it continues:
There have been many species of human-like creatures in the past. Now, all but Homo sapiens are extinct. (Caird)
This is a very important statement. Let me repeat it. "There have been many species of human-like creatures in the past."
You mean there are none today? No, only homo-sapiens! So in the search for truth, according to this textbook, Ape Man, we are going to reconstruct the creatures who lived in the past that were on their way to becoming man. They are all extinct. There is not one that you can find anywhere in the world today that is alive. We have these ape-like creatures and we have man. But there is nothing in between that is living. They all lived in the past. And so in the search for truth for human origins, we have to reconstruct what they look like.
It continues:
If we can understand the past, we may be able to understand why we are the way we are today and perhaps we can find clues to our future. (Caird)
We have all seen these representatives that supposedly existed in the past. Remember? There are none alive, so they have to be reconstructed. Well, in some cases we are going to see they were fabricated.
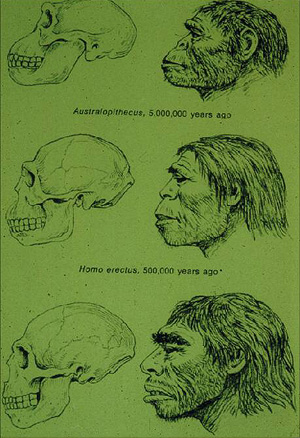
Here is a typical illustration showing the lineage of man.
Over in the left-hand, bottom corner we see an apelike creature squatting on the ground. The next one, well, obviously he is standing up. And then in the next picture, he is becoming a little bit more modern. And on the right-hand side, we see sort of a caveman-looking kind of creature, but he is on his way to becoming a modern man.
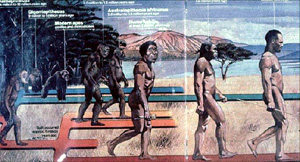
National Geographic typically promotes the evolutionary view of human origins. And here in this mural, we see two different groups of human beings at different layers or levels of the evolutionary development.
On the right-hand side, we see a group of people and they are hunting with sticks and stones. But on the left-hand side, they are a little bit more primitive because they just have bones. See this gives the impression that as we go back in time, our ancestors were more primitive.
Scientists attempt to reconstruct what our ancestors looked like based on fragments of fossils.
Here we see an example taken from the book, Ape Man, how Homo Erectus was reconstructed. Notice there is a skullcap and a portion of a skull. And then on the right we see, that the scientists were able to reconstruct the fleshy features of the face. And also they were able then to reconstruct the whole society by showing us this painting and what they were doing. And by the way, the scientists even know exactly when they lived.
As we look through various textbooks on the subject of human origins, we are bombarded with paintings and illustrations of what these extinct ancestors looked like and how they lived. And by the way, there are many people who get their science from Hollywood movies. But again in reality there is a lot of speculation. Unfortunately many people embrace it as fact.
Here is a Time Magazine cover.
This goes back to the late 1970s when Richard Leakey was a fairly young man. He is squatting next to an African native who is wearing a Hollywood mask. Notice the subtitle on the front page, "How Man Became Man." Richard Leakey was not satisfied with the way Hollywood artists had made the mask to represent what he believed Homo Habilis looked like. It took several attempts. So what you are seeing here is an African native wearing a mask. Is that really valid in terms of supporting the evidence of how we have evolved?
On the front cover of Discover Magazine we read, "The Ape in Your Past, He Is a Lot Closer Than You Think." You see popular magazines and journals are constantly bombarding us with this information relating us to the apelike creatures, saying that we have evolved. "How Apes Became Human," on the cover of Time Magazine, July 23, 2001—"What a new discovery tells scientists about how our oldest ancestors stood on two legs and made an evolutionary leap."
Here is a textbook which I purchased at the university where I used to take classes and teach. It is entitled, The Human Odyssey: Four Million Years of Evolution by Donald Carl Johansen, PhD, Institute of Human Origins. And in the foreword we read this statement:
Education is the great liberator. It frees us to think objectively. My studies have taught me to respect the natural world. They’ve also taught me that all humans have a common origin and therefore a common destiny, the outcome that will be determined by humankind itself. We do have a capacity to make the future a long and fruitful one only if we take the time to learn who we are and how we fit into the natural world. (Donald Johanson, Ph.D.)
Of course Johansen is quite famous in his proposal of ape-men creatures (one of them is Lucy).
In this book, The Human Odyssey, we are given a number of suggestions of what our ancestors may have looked like. By the way, these are paintings of linear-like creatures. And according to this textbook, yes, these are cousins.
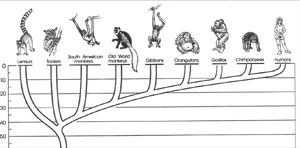
As you see in this lineage we have lemurs, tarsiers, South American monkeys, Old World monkeys, gibbons, orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees and humans. And there you see the common connection, according to the idea of evolution. This is what is taught in universities as acceptable in terms of human origins.
Well, what I would like to do in this particular session is to look at some of the claims that have been proposed in the past of the lineage of man; that is the "so-called intermediates" between the ape creatures and mankind. And there are many of them. We can only look at a few, so we will choose some in this proposed lineage of man.
Notice on the left-hand side is the monkey-like creature and on the right-hand side is modern man. And remember in the introduction of Ape Man—"There have been many apelike creatures that have lived in the past but they are all extinct." So let us examine some of the claims.
Here is one that was proposed a number of years ago as a credible link in the Ape Man lineage
.It is called Ramapithecus. Ramapithecus was first formulated based on two portions of jawbone. One was found in Africa and the other in Turkey. And they thought the teeth were more humanlike than apelike, so from this Ramapithecus was reconstructed. There we have the painting. Notice what Ramapithecus looks like. Well, they seem to know a lot of details. They can see how long his arms were, how stooped over he was when he walked, how much hair on the body, the features of the face, and even the length of the large toe.
Science Digest, April 1981 states,
Nevertheless, a reinterpretation of Ramapithecus’s humanlike jaw by David Pilbeam of Yale, one of the experts on the species, now suggests that Ramapithecus was an ancestor of neither modern humans, nor modern apes. Instead, Pilbeam thinks it represents a third lineage that has no living descendants.
So at one time it was in the lineage of man. It was removed and for this reason.
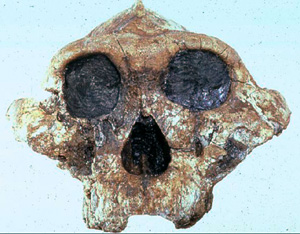
Then we have Australopithecus. Australopithecus was found in the early 1900s by Dr. Dart and by Dr. Louis Leakey.
And as you can see from this skull, it does not look humanlike at all. But they believed that it deserved a place in the lineage of man and that it was on its way to becoming man. And certainly the artists were able to reconstruct from the skull and other fossil remains what Australopithecus may have looked like. And again we see this painting of a creature who is part ape and part human. From the book Ape Man, well now we have a portrait. But again, keep in mind what you are seeing. These are paintings done by modern artists, attempting to explain what our ancestors looked like in the past.
And notice on the left-hand side of the screen there is a whole family of these part-ape, part-humanlike creatures based on fossils that do not look human in any way.
Richard Leakey, the son of Louis Leakey, removed Australopithecus from the chart in the late 1970s. And it made his father so angry because his father was the one who had placed Australopithecus on the chart, and he quit speaking to his son for several months. Here we see on this particular chart, Australopithecus that was removed.
Donald Carl Johansen (who wrote the forward of the book, The Human Journey, that I mentioned earlier) discovered Lucy. And Johansen said, "Well, Lucy is an Australopithecus. It belongs in the lineage of man." And so he was in a great debate with Richard Leakey, saying that for sure this fossil that he discovered proved conclusively that Australopithecus was on its way to becoming modern man. He said this was based on the knee joint and also the hip joint. showing that it had walked upright. And other anthropologists who are evolutionists suggested that Lucy is nothing more than like a chimpanzee and it does not deserve a place in the lineage of man.
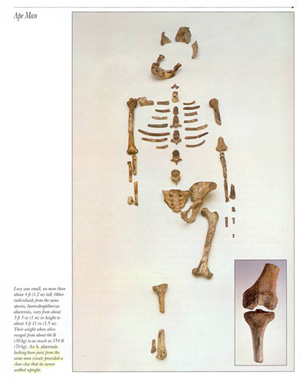
In the book, Ape Man, we see this photograph of the fossil of Lucy.
And you will notice it is only a partial fossil, that there is not a complete knee joint. But also notice that in the bottom right hand corner of this page there is a knee joint. Why is that there? Well, if you read carefully in the fine print over on the left-hand side, you will read this statement: "An afarensis locking knee joint from the same area (inset) provided a clear clue that its owner walked upright." You see, when Johansen was traveling around the country giving lectures on Lucy being in the lineage of man, he carried this knee joint with him. And on one particular occasion he was asked by someone who was at attendance, where he found the knee joint. He reluctantly told them the knee joint was found two miles away in a strata two hundred feet lower. It was not even found with the fossil. So, often we see that some of these paleontologists do everything they can in order to try to support their views that these apelike creatures belong in the human lineage. This is not always based on fact and truth.
In the book Ape Man, we see this group picture of Lucy and her relatives, showing Lucy coming out of the trees and beginning to walk upright. But again, this is not a photograph. It is merely an artist’s representation.
When we look back historically regarding how this lineage of man came about, it is important to go back to the time of Ernest Heckles, shortly after Darwin wrote his book The Origin of Species. Charles Darwin had laid out the idea that through time there is a progression from lower to higher, from simple to complex. And although he did not state clearly that humans had evolved from monkeys, of course it was inferred. And one of his greatest supporters was a German zoologist by the name of Ernest Heckle. Ernest Heckle was convinced that Darwin was correct. In fact, he was willing to propose it would only be a matter of time when a missing link would be found showing the connection between apelike creatures and humans. And this is how the first fossil of Homo Erectus was discovered.
First of all, let me point out to you that Ernest Heckle was so enthusiastic that there would be a link found between apes and humans, he decided to have one reconstructed before anything had been found. That is, he hired an artist to paint what the missing link would look like when it was found.
And here we have the famous Pithecanthropus allus and his mate, and also a child. Ernest Heckle commissioned this painting of the missing link before anything was found.
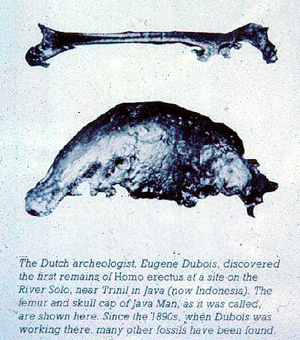
Now Ernest Heckle had a graduate student by the name of Eugene Dubois. And Eugene Dubois was instructed by Heckle to find the missing link and he even told him where he would likely find it in Indonesia. And this is how Homo erectus first came about. Dutch archaeologist Eugene Dubois went to Java Indonesia but Dubois himself actually did not find these fossils. He hired some ex-convicts who were out on parole to go out and do the digging.
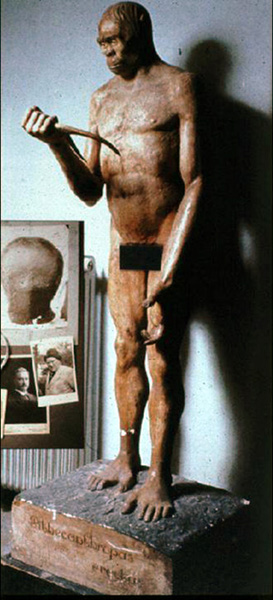
They found a skullcap of a gibbon and then the following year, fifty feet away in that same location, a human leg bone and some molar teeth. Dubois was reluctant to announce that he had found the missing link. But later, after discussions with Ernest Heckle, he was convinced that he had found the missing link. And so, Java Man first appeared. And here is a model of Java Man based on the skullcap of an ape and a human leg bone. Before Dubois died he admitted publicly actually what he had discovered.
Here is a model of Pithecanthropus erectus, Java Man—which I took a picture in a museum of natural history in Beijing, where it stands today.
Then we have Neanderthal. Neanderthal is commonly considered to be one of these creatures that is evolving on its way up to become a modern man. It is rather brute-like. When the first fossils of Neanderthal were found, they saw that the brow of the skull was somewhat pronounced. The joints were enlarged. And so it was announced that a missing link had been found between apes and humans. It is a brute-like creature that existed in the past, on its way to becoming modern man. And this was one of the first depictions of Neanderthal.
And you will note it is very brute-like, very apelike, and he is carrying a club.
Numerous fossils of Neanderthal have been found and also scientists have reconsidered their interpretation. The brain capacity of Neanderthal actually is larger than ours! But they have also discovered that the reason there was a brow pronouncement and the joints were swollen was because this was a group of people that suffered from some kind of dietary deficiency. It was perhaps a bone disease like rickets.
Modern man is no different than Neanderthal other than these joint enlargements. And Neanderthal, as I said, has a larger brain. So there has to have been a reinterpretation.
And now we see Neanderthal—he has lost a lot of hair. Instead of a club, he carries a sharpened stick.
See this search for the truth on human origins has covered nearly every continent. And in America there has also been a contribution which is somewhat of an embarrassment. In the ‘30s, in Nebraska, a tooth was discovered. And scientists, at the time, thought they had found clear evidence of an apelike creature on his way to becoming man. And in the ‘30s, the London Daily Times which is a British newspaper, published this illustration or drawing of Nebraska Man.
And there you see Nebraska Man and his wife Nebraska Woman. Later, it was determined that from this single tooth the Nebraska Man had been reconstructed, and that tooth was actually the tooth of an extinct pig. So in America, the attempt to come up with a missing link failed.
Then we can go to Great Britain. For years a model of the Piltdown Man stood in the British Museum of Natural History, as a trophy to Darwinian evolution. Piltdown Man was found in the area of Piltdown in southern England. I have been there on a couple of occasions. Charles Dawson, who was an amateur biologist, found a skullcap in a gravel pit not far from his home. Later, when digging in the same pit he found a jawbone. He thought it was kind of an apelike jawbone and of course he put the two together and the jawbone along with the skull formulated Piltdown Man. Later upon closer investigation it was discovered the jawbone actually was the jaw of an ape. The teeth had been filed to make them look humanlike. The whole thing was a fraud. To this day, no one is quite certain what happened; whether it was Dawson himself who did this, or if somebody planted the jawbone in the pit and later that this became evidence supposedly for evolution—that is still in question. But whatever the case, Piltdown no longer is even considered to belong in the lineage. It too has been an embarrassment to the evolutionary community.
But constantly we see that this theory is being upgraded. And if you follow the news, whether it be through magazines, or journals or television news, you will see that almost monthly there is some new discover that is found, somewhere in some place. They are always finding something a little bit older than the last fossil that was found.
Let me give some examples. The cover of Time Magazine, August 23, 1999 reads, "How Man Evolved—Amazing new discoveries reveal the secrets of our past." And in this magazine we have this article: "Up from the Apes—Remarkable new evidence is filling in the story of how we became human." And again as we have mentioned, we require more than a story, we need evidence.
Here in the magazine we have the lineage now reconstructed: "How We Got from There to Here." And we note this statement: "Common ancestor—No fossils found yet, but scientists believe the human and ape lines diverge between six and four million years ago." There we see many of the examples we have already discussed. Some are still placed in the lineage of man, claiming that these are credible fossils, part ape and part human. The fossil that was found is listed as number one. It is called Ardipithecus ramidus. It was discovered by a Japanese anthropologist who was walking in a desert in Africa and looked over his shoulder at noon and saw a tooth in the distance. And as he states, I quote: "I knew immediately that I had found a very important hominid fossil." He said this even before he picked it up! They claim that it fits into this period of time—a little over four million years ago.
Now let’s look at another article which is more recent, from July 23, 2001: "One Giant Step for Mankind: Meet your newfound ancestor, a chimp-like creature that stood up and walked 5.8 million years ago." So now you see that in just a few years, another discovery has been made and they have found a fossil that is older than the previous one—from 4.4 million now to 5.8 million years ago. And this is called the newfound ancestor. But where did they find him? Well, this is rather interesting. Time Magazine shows us the location, it is called Ground Zero. "Scientists scour barren African hills where humankind was born in more fertile times, millions of years ago." And I want you to note what this area looks like. It is an area that shows vast devastation from volcanic destruction. And there on the side of the hill, you see a group of scientists and they are looking for fossils. In fact, they are panning for fossils. There you see one of the scientists who has a pan. He is shaking through and he is looking for fossil evidence to prove that we have evolved from brute-like creatures. And sure enough, he discovered something! What did he discover? A single toe bone! And from this single toe bone, these scientists were able to reconstruct our newfound ancestor.
You see, these are the facts. I am not making this up. My objective of showing you this is to have you think critically. But unfortunately, most people do not think critically. There it is on the page: "This Toe Bone Proves the Creature Walked on Two Legs." Well, I need more evidence. Remember in this lineage between apelike creatures and man, the ancestors are all extinct. There are none alive today. They lived in the past and now they have to be reconstructed.
Then we have another discovery, from Time Magazine, July 22, 2002—"Is This Our First Ancestor?" And yes sure enough, now scientists have gone back seven million years! In the previous session I presented to you how they claimed they found out it was that old. They could not even date in the area radiometrically. They had to look at the fossils that were there and then find another area where there were fossils and date that location with radiometric methods. And they have come up with this period of time they think is approximately seven million years old. And now we have one that is the oldest that has ever been found. And he is the father of us all. Is this really true? And once more the lineage goes back further and further in time as the new kid in the block, as they say, has come on the scene. And many people are convinced.
Richard Leakey, whom I have mentioned quite often in this series, in 1982 made a statement and I think this statement is a fair statement. He said he once believed that we could trace the lineage of man back fifteen million years. But he came to this revelation one day that that was impossible. He said he had made a twelve million year error. He said the furthest we can go back in time to trace our ancestors is 3.75 million years. In other words, here is a scientist who says, "You know I used to believe this, but now I don’t. I have made a mistake." That is good! But is he even correct in saying we can go back 3.75 million years? And if so, what did they find? Well, they found footprints. And these are the famous footprints found by his mother, Mary. By the way, isn’t it interesting that Louis Leakey, Richard Leakey, and Mary Leakey (father, son, and mother), these three people have shaped the minds of billions of people with their theory.
Well, Mary Leakey took some measurements of a footprint found in volcanic material in Kenya. And they dated this material and that is where they came up with this age of 3.75 million years. Remember they have dated the lava dome at Mount St. Helens that was formed in 1980 and since and it dates millions of years. Are these dates accurate? Well, I think they are questionable. Well, there are the footprints and this is what Richard says: "These footprints are the best evidence we have of what our ancestors were like. And we can trace our lineage back to them."
Here is the area in which these footprints were discovered. And I want you to notice there is only a very small amount of material above the volcanic layer—just a few inches of turf. That has been removed and there you can see the scientists observing the footprints. And there are other footprints. You will notice in this photograph there is a left, right, left, right, left, right, left by the alleged ancestor as he walked through the volcanic material when it was soft. Just as if you were to walk down a wet cement sidewalk and leave your footprints there. And in fact, if you did they would have been exactly the same! Why do I say that? Well, notice in the insert there is a man standing next to one. And his pant leg is rolled up and his sock is removed. And the National Geographic states: "The form of his foot is exactly the same as ours."
Now in the English language the word exactly means exactly. It is the same! So that is why I say, if you were to walk in this region today and that material was like a wet cement sidewalk and you had your socks removed and you walked down this area, you would leave exactly the same footprints. They would be identical.
Now National Geographic helped sponsor the Leakey Foundation as they were doing the research here. And this was a major discovery. So National Geographic invited an artist by the name of Jay Matterness to come to the location. He does a lot of artwork for various museums along with the tracker who had identified the other footprints. And there were many different footprints along with these alleged human footprints, so the tracker identified the footprints and then Matterness did the artwork to reconstruct what it looked like 3.75 million years ago. And here is the painting.
In the footprints that look like Guinea fowl, the artist painted Guinea fowl and they look exactly like Guinea fowl look today. In the footprints that look like giraffe footprints, the artist painted a giraffe and it looks identical to a giraffe that you would see today, anywhere in any zoo. In the footprints that look like elephant footprints, well the artist painted a herd of elephants and they look like elephants. In the rabbit footprint, the artist painted a rabbit just like a modern rabbit. And off to the side, it is difficult to see, there is an ostrich that was painted because there were ostrich footprints there. But in the footprints that are identical to ours (the same, with no difference) the artist painted two adult baboon, part-humanlike creatures without any clothes. One is carrying a baby, the other a stick. There it is in the name of science. But is this science or is this an interpretation of the evidence that shows strong bias to support the evolutionary assumption?
Richard Leakey says, the farthest back we can go to prove the validity of our human origins is to these footprints. But what was in the footprints? Do you trust the painting? I do not. By the way, I had to censor this particular one. But if you go to the Museum of Natural History in New York, this is what you will see. These are the models based on those footprints. And just last fall when I was in New York City, I went to the museum. I was standing in this very location and a professor and part of a university class came by. And the professor was pointing to these models and he said, "How can anyone not be convinced?" It is amazing! People do not think critically.
We have been looking at the lineage of man—this belief that we have evolved. Remember from the introduction of the textbook, we were told there are no living intermediates. They are all extinct. My question is, were there any intermediates? Did they exist? Or is this something which is simply in the minds of men? A way of attempting to explain our origins based on evolution.
In The Human Odyssey, which we read from the introduction earlier, we read this following statement: "The concept of evolution stands as one of the greatest ideas ever formulated by the human mind." Really? I believe that evolution was formulated by the human mind but it was inspired spiritually. Yes indeed, Charles Darwin’s theory that proposed a way to explain away the Creator has been widely accepted. The statement by Donald Carl Johansen continues: "Through this book and the exhibit on which it is based, you will learn to better understand some of the questions all of us have asked some time in our life. Who are we? How did we become what we are? How do we fit into the natural world?"
Several years ago on my way back from Russia, as I was traveling through London, a friend of mine went with me to the British Museum of Natural History. I try to go there as often as I can. And I was standing there in a portion of the museum on the second floor devoted to the Ape Man lineage. And while we were standing there looking at the display, a mother and her daughter—I would say she was about five years old—came and stood in front of us. And the mother was reading some of the explanation on the display cards to her daughter. And her daughter said, "Mommy, that’s not the way God created us." The mother continued to read the evolutionary explanation. The little girl said, "Mommy, Adam and Eve were not apes." And the mother said, "It’s okay if you believe in God and the Bible. You’re just a little girl. I used to believe in God and the Bible but now I believe in evolution and you will too when you get older." Do you know that coded into a child is a knowledge and understanding that there is a Creator? Do you know that much of the education community is geared to reeducating children so that they would disbelieve that there is a Creator. They are geared to believe in man’s speculation and refuse to acknowledge God’s clear revelation? That is exactly what is taking place.
Roger Lewin, from his book Bones of Contention, page 348, states the following:
It is an unfortunate truth that fossils do not emerge from the ground with labels already attached to them. And it is bad enough that much of the labeling was done in the name of egoism and a naïve lack of appreciation of variation between individuals. It remains inescapably true that applying the correct label is astonishingly difficult, not least because such labels are in a sense, arbitrary abstractions. Especially so with the material on which the analysis is being done is fragmentary and eroded. ‘It is an incredibly difficult problem,’ says Lord Zuckerman. ‘It is one so difficult that I think it would be legitimate to despair that one could never turn it into a science.’ (Lewin 348)
Lord Zuckerman is not a creationist. He is saying that these interpretations, these labels that we put on the fossils, are not legitimate. They are not science.
And I am reminded what Paul said to Timothy, "Be cautious of science, falsely so called" (1 Timothy 6:20). There are billions of people today in the world who do not believe there is a Creator, therefore they do not believe there is a Redeemer because they believe in evolution. They have been taught to believe in evolution. And I believe they have been deceived.
O Timothy, keep that which is committed to thy trust, avoiding profane and vain babblings and oppositions of science falsely so called, which some professing have erred concerning the faith. Grace be with thee. (1 Timothy 6:20-21)
In summation, that is the evolutionary view of our human origins. In our next session we want to talk about God’s view—His revelation given to us from Scripture. And we are going to see, just as we read from Isaiah 55 that as high as the heavens are above the earth, so is God’s view on human origins than man’s view.
Bibliography
- Caird, Rod. Ape Man; The Story of Human Evolution, 1994
- Time Magazine, "How Man Became Man", November 7, 1977
- Johansen, Donald C. The Human Odyssey; Four Million Years of Human Evolution
- Discover Magazine, "The Ape in Your Past, He Is a Lot Closer Than You Think"
- Time Magazine, "How Apes Became Human", July 23, 2001 pgs. 54-55
- Time Magazine, "How Man Evolved", August 23, 1999
- Pilbeam, David. Science Digest, "Ramapithecus’ Humanlike Jaw", April 1981.
- Time Magazine, "Is This Our First Ancestor?" July 22, 2002
- Roger Lewin., Bones of Contention, page 348
- Matternes, J.H. National Geographic, "People and Places of the Past", 1982.
Thank you for reviewing this lecture brought to you by Blue Letter Bible. The Lord has provided the resources, so that these materials may be used free of charge. However, the materials are subject to copyrights by the author and Blue Letter Bible. Please, do not alter, sell, or distribute this material in any way without our express permission or the permission of the author.
We invite you to visit our website at www.BlueLetterBible.org. Our site provides evangelical teaching and study tools for use in the home or the church. Our curriculum includes: classes for new believers, lay education courses, and Bible-college level content. The lectures are taught from a range of evangelical traditions.
For any questions or comments please feel free Contact Us.